NVIDIA Spatial Intelligence Lab
Introduction
Welcome to the homepage of the NVIDIA Spatial Intelligence Lab led by Professor Sanja Fidler. Established in 2018, our research group is primarily based in Toronto.
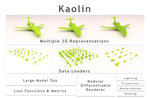
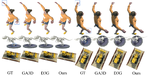
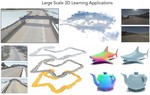
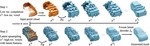
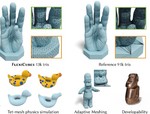
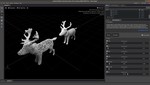
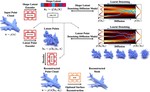
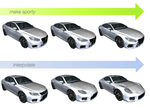
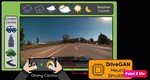
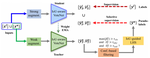
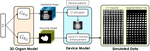
Our focus is on advancing spatial intelligence, with particular interest in 3D Content Creation (including Reconstruction and Gen AI), Geometry Processing, Physics Simulation, 3D perception, and Physical AI.
As of April 2024, we have proudly joined forces with Ken Museth and his physics research team. Since December 2024, we also welcome the addition of Laura Leal-Taixe’s team to our lab.
We invite applications for the following positions:
- full time research scientist
- full time research engineer
- research scientist intern
- research engineer intern
See this link for open positions, or contact our members for more details.